Adapting our baby formulas to comply with new legislation
New EU legislation* has been introduced that affects all infant formula, follow-on formula and infant foods for special medical purposes (FSMPs). This legislation is effective from February 2020** and reflects updates to previous regulations and the latest science to give babies the best start. All baby milk manufacturers must adhere to this legislation.
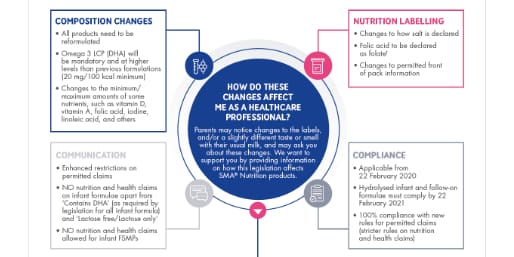
HOW DO THESE CHANGES AFFECT ME AS A HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL?
Parents may notice changes to the labels, and/or a slightly different taste or smell with their usual milk, and may ask you about these changes. We want to support you by providing information on how this legislation affects SMA® Nutrition products.
COMPOSITION CHANGES
- All products need to be reformulated
- Omega 3 LCP (DHA) will be mandatory and at higher levels than previous formulations (20 mg/100 kcal minimum)
- Changes to the minimum/maximum amounts of some nutrients, such as vitamin D, vitamin A, folic acid, iodine, linoleic acid, and others
NUTRITION LABELLING
- Changes to how salt is declared
- Folic acid to be declared as folate†
- Changes to permitted front of pack information
COMPLIANCE
- Applicable from 22 February 2020
- Hydrolysed infant formula and follow-on formula must comply by 22 February 2021
- 100% compliance with new rules for permitted claims (stricter rules on nutrition and health claims)
COMMUNICATION
- Enhanced restrictions on permitted claims
- NO nutrition and health claims on infant formula apart from ‘Contains DHA’ (as required by legislation for all infant formula) and ‘Lactose free/Lactose only’
- NO nutrition and health claims allowed for infant FSMPs
SMA® Nutrition has already started to implement this new baby formula legislation across our product range. We will continue to update remaining formulations to ensure compliance by 22 February 2020.**
For more information on product changes please visit our product range section by clicking on the link https://www.smahcp.co.uk/formula-milk or to speak to a member of our SMA® Nutrition Careline team please call 0800 0818180 (UK) or 1800 931832 (Ireland)

Read full article
DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; FSMP, food for special medical purpose; LCP, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids.
* Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/127 on infant formula and follow-on formula, and Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/128 for food for special medical purposes.
** All infant formula, follow-on formula and infant FSMPs must comply by 22 February 2020; infant formula manufactured from protein hydrolysates must be compliant by 22 February 2021.
Dietary Folate Equivalent (DFE): 1 μg DFE = 1 μg food folate = 0.6 μg folic acid from formula.